Guided: Collaborative robots reflect the latest trends in robot development. They are more adaptable to the requirements of robot flexibility and perception, and the flexibility, adaptability and problem-solving capabilities of humans and the power of robots. The combination of durability and accuracy of motion brings model innovation to the production and assembly process, which allows Chinese robotics companies to see the opportunity to “get rid of the role of followersâ€. Chinese collaborative robots have the opportunity to “overtakeâ€.
Collaborative robot market prospects
In 2014, ABB, one of the “four major families†of industrial robot manufacturing in the world, launched the world's first collaborative robot, YuMi, which opened a new chapter in industrial robotics. In the future industry 4.0 era, the production line in the smart factory is more flexible, and the robot needs to share a working space with people. The human-machine cooperation robot is expected to become the next growth point in the robot field.
YuMi of ABB, Switzerland

A collaborative robot is a robot that can directly interact with humans in a certain area. The operation of the cooperative robot is relatively simple, and it is a branch of the industrial robot. It is also more expensive in price than the traditional industrial robot.
The rise of collaborative robots means that traditional industrial robots must have some deficiencies or are unable to adapt to new market demands. There are three main points:
First, the cost of deploying traditional industrial robots is high;
Second, traditional industrial robots cannot meet the needs of SMEs;
Third, it is unable to meet the needs of emerging collaborative markets.
Compared with traditional industrial robots, collaborative robots are not in a class with them. In order to achieve the purpose of "collaboration", the working distance between the robot and the human can not be too far. Therefore, the size of the cooperative robot is small, and can even be placed directly on the workbench.
In addition to the speed and accuracy of traditional industrial robots, collaborative robots have some advantages that traditional industrial robots do not have, such as light weight, safety, low price, high flexibility, friendly operation interface and human-machine cooperation. It not only makes the production process of large enterprises go up to the next level, but also opens up new opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises that are still in the process of automated production.

Baxter from ReThink RoboTIcs is a new generation of collaborative industrial robots
Regardless of whether it is from the market or the technical level, collaborative robots have irreplaceable advantages and market prospects, which is already a major trend in the future market.
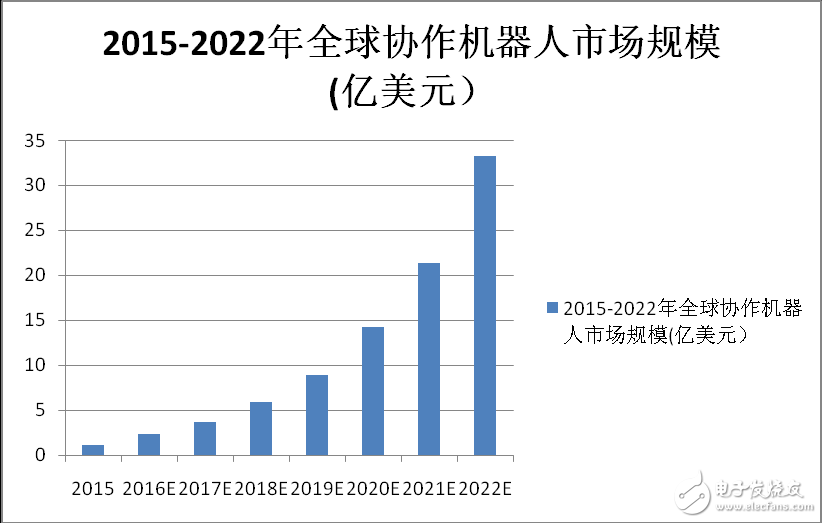
According to analyst firm MarketsandMarkets, it is expected that between 2016 and 2022, collaborative robots are expected to grow 60% year-on-year, from nearly $110 million in 2015 to more than $3.3 billion in 2022.
Collaborative Robot Industry Specification
The orderly development of collaborative robots is inseparable from industry norms and safety standards. In May 2013, the American Robotics Industry Association (RIA) announced that new robot safety standards have been approved by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
The new ANSI/RIA R15.06-2012 version standard is an upgraded version of the 1999 version standard, equivalent to the international ISO 10218:2011 robot safety standard. One of the important upgrades to internationally equivalent standards covers the collaborative work of people and robots.
This standard sets four requirements for collaborative robotic operations to ensure that personnel can be close to a running robot without a safety net. Robots in cooperative mode must meet one of the four requirements of the standard:
Safety Level Monitoring Station - This mode of operation requires the robotic system to monitor the work area and stop all actions when someone enters the collaborative work area. This monitoring may involve using a laser to monitor if someone is crossing the edge of the work area, switching to monitoring whether the enclosed space opens the door, and the like.
Manual teaching - such robots do not have autonomous functions and require a worker operator to control every movement of the robot. The speed of the movement is also monitored and maintained within the safety limits of the robot's internal system.
Speed ​​and Separation Monitoring - Robots monitor and limit their speed of movement in this way and monitor the distance between individual components and workers in the collaborative work area. The robot's movement must remain outside the minimum distance from the worker, or when the worker is too close, the robot will stop moving.
Power and Power Limits - When such robots are designed for motion speed and power limitations, built-in sensors can detect when it comes into contact with workers or other objects. When a similar contact occurs, the speed and power limits will cause the collision energy to be insufficient to cause serious injury.
The International Committee drafted the ISO Technical Specification (TS) 15066 as a guide to the use of this standard in a collaborative work mode. The specific content is still under technical development. After the development is completed, it needs to be recognized by the industry to supplement the ISO10218 safety standard.
Through this series of definitions, the operation of collaborative robots is no stranger. Traditional industrial robots can also perform the functions of the first mode when the appropriate work area limit monitoring sensor is configured and programmed to achieve the proper response. However, robots that have been running in the fourth mode have begun to work in an unrestricted environment. Such robots are usually assembled for small parts or require high precision for repeated material handling. Often these characters include assisting workers in automating their daily tasks, while workers deal with operational tasks that need to be judged or not easily replaced by robots.
Collaborative robots currently come in several forms. One of the most common is that a single robotic arm is attached to a workbench, wall or ceiling and can be extended into the work area. Similar to Rethink RoboTIcs' Baxter robot and ABB's YuMi, the exterior is more human-like, with two robotic arms, a torso, and even a "head." This robot can stand alone, be able to operate on a workstation like a worker, and therefore more easily enter the factory assembly line like a worker. Others, such as Kawada's Nextage, have wheels installed for quick redeployment.
Fiber Optic Box,Fiber Optics Box,Fiber Optic Boxes,Fiber Optic Junction Box
Cixi Dani Plastic Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.danifiberoptic.com
