Overview
Audio processing is very important for consumer electronics applications such as mobile phones and tablet computers and other mass-produced products. Area and power consumption are often the key design criteria, and the market requires high-quality high-fidelity (Hi-Fi) audio effects. Integrating silicon-proven and optimized audio IP to achieve specific audio functions helps reduce the power consumption, area, and cost of today's multimedia chip systems.
As the design gradually transitions to the 28-nanometer process technology, the challenge of integrating audio functions becomes more complicated because the analog circuits do not follow Moore's Law and will not decrease in size as the process develops. The cost of wafers using the 28-nanometer process will be much higher than the 65-nanometer or 40-nanometer process technology. Digital circuits follow Moore's Law. Although the cost of wafers has increased, its performance and density have also increased. The analog circuits used in audio codecs generally use IO devices, so they will not use core devices like digital circuits to reduce size. In this way, while the wafer cost increases, the inherent performance of the analog circuit has not improved, and the area has not been reduced. Therefore, a new architecture must be developed to reduce the total area. For example, an audio codec with a 65-nanometer technology and an area of ​​2.5 square millimeters needs to be reduced to 1.9 square millimeters after using 28-millimeter technology to keep the silicon cost the same. It is this 25% reduction in area that constitutes a key challenge for the audio codec of advanced process nodes.
This article examines the major system and technical challenges faced by integrating audio functions on a 28-nanometer mobile multimedia chip system, and how to address these challenges through the following technologies:
Use Moore's Law to change some functions from analog to digital;
· Flexible design, support the audio sampling rate of the chip system common reference clock;
· Make a good balance between power supply voltage reduction and performance;
· In-depth understanding of the system function division outside the chip system;
Recognizing that there are measures to minimize system costs, designers and system architects will be able to discover an effective balance between cost, functionality, and performance, enabling them to embed audio IP decoder solutions to help their SOC compete Win.
Basic knowledge of audio codec
The audio codec is mainly composed of two types of data converter modules, namely an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for recording and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) for playback. For stereo or multi-channel decoders, these modules are copied separately. Figure 1 is a block diagram of a typical stereo audio codec. Figure Chinese recording channels include an amplifier with volume control, which can adjust the small signal microphone and large signal cable to the input range of the analog-to-digital converter. The playback channel includes the ability to directly drive headphones or small speakers for amplification, and each channel has a volume control function. There is also a low-noise power supply that provides microphone bias.
The digital circuit is composed of multiple parts. The most important thing is the digital audio filter, which can convert the data rate to the oversampling clock of the data converter and eliminate the high frequency noise outside the audio band. Clock management is also important. It ensures that modules of different rates are synchronized with each other and supports multiple sampling rates.
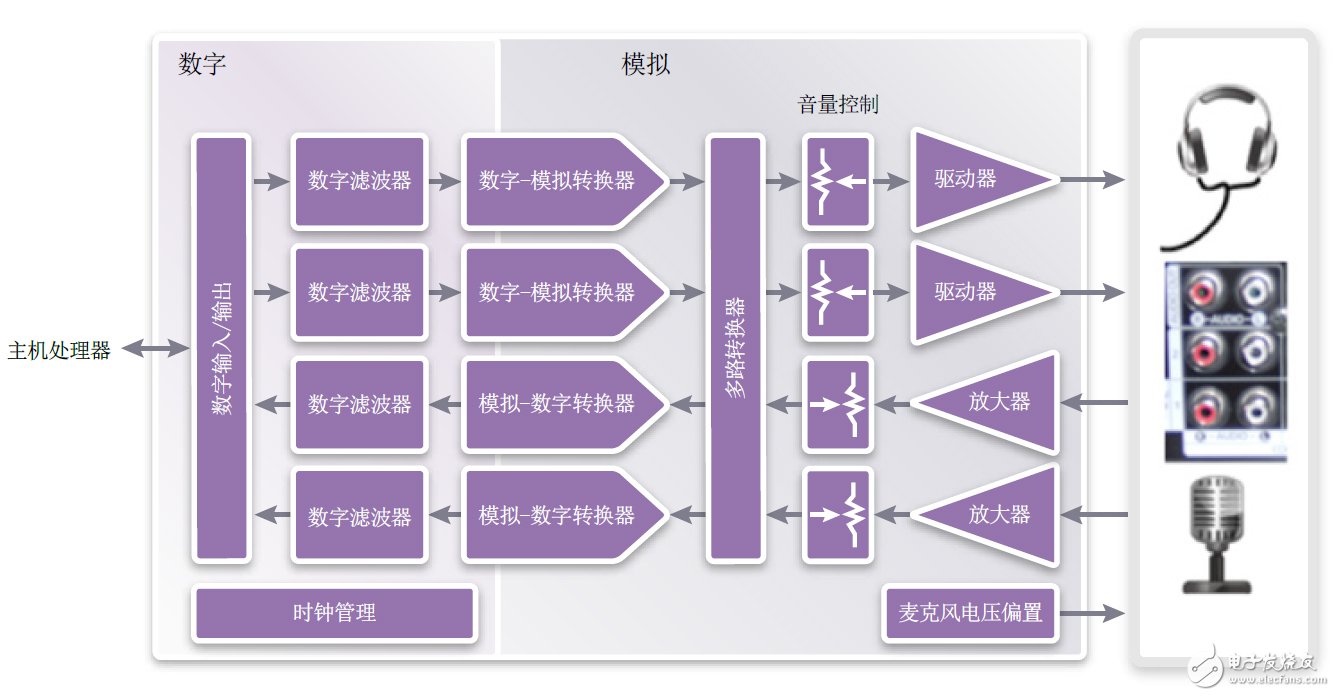
Figure 1: Functional block diagram of the audio codec
To use the 1.25mm Ribbon Connector, you will need to first ensure that the ribbon cable is properly aligned with the connector. The pins on the connector should be lined up with the corresponding holes on the ribbon cable. Once the cable is properly aligned, you can then insert the connector into the corresponding socket on the device.
Overall, the 1.25mm Ribbon Connector is a reliable and versatile connector that is widely used in the electronics industry. Its high-density design and compatibility with ribbon cables make it an ideal choice for many applications
1.25Mm Ribbon Connector,Pressure Terminal Connectors,Pressure Terminal Connector,Pressure Connectors
YUEQING WEIMAI ELECTRONICS CO.,LTD , https://www.weimaiconn.com
