Since the 1990s, China has successively introduced different types of missiles from Russia, and at the same time, it has also introduced supporting missile test systems. In recent years, as the life of the missile test system is approaching, extending its service life on the basis of existing domestic technology is an important task of the maintenance support department. To this end, the development of spare parts for key components of the missile test system has become an important means of extending the life of the system.
According to the requirements of a certain type of missile test equipment, a multi-channel control circuit based on ISA bus is designed and developed: this circuit integrates 16 photoelectric isolation input channels and 8 single-pole double-throw (SPDT) relay output channels, each input or The output channels are equipped with indicator lights to identify the current status in real time. In the test system, the control circuit can distribute the data signal, command signal and power signal to different circuits under the control of the ISA test bus to achieve automatic testing of the missile. The actual application results show that the developed multi-channel control circuit meets the design requirements and can completely replace the Russian-made circuit.
1 Introduction to ISA bus
The ISA (Industrial Standard Architecture) bus was formed by IBM in 1984 to further expand the XT bus standard. ISA bus standard supports 24-bit address line, 16-bit data line; supports 11-level interrupt IRQ3 ~ IRQ7, IRQ9 ~ IRQ12, IRQ14 ~ IRQ15; supports 7 DMA transmission channels DRQ0 ~ DRQ3, DRQ5 ~ DRQ7; supports master-slave control , I / O wait and I / O verification and other functions. In order to maintain backward compatibility with the XT bus, the ISA bus has made special arrangements in the definition of signal functions and physical interfaces, that is, keeping the original XT bus unchanged, adding a 36-wire connection slot, divided into C, On both sides of D, the expanded functions are designed on the signal lines on both sides of C and D. The pins are defined as follows:
1) Data bus SD7 ~ SD0 SD7 ~ SD0 is an 8-bit bidirectional tri-state data bus, which transmits commands, data and status between the chip and the main interface. SD7 is the highest bit.
The register selection pins are SA9 ~ SA4, SW DIP-6 (board base address 011001) and AEN #. These pins determine whether the conversion responds to the I / O cycle. When AEN # is logic low and SA9 ~ SA4 and 6 When the value of the toggle switch is completely matched, a selection signal is generated internally to make the conversion respond to the I / O cycle.
2) Address signals SA3 ~ SA0 are used as register selection signals in the FPGA chip on the conversion circuit during I / O read and write operations.
3) During the write operation of the read and write signals IOR # and IOW #, the data is latched at the rising edge of IOW #. During the read operation, when IOR # is valid, the conversion module directly drives the 8-bit data line.
4) Interrupt signal INTR When an enabled interrupt in the interrupt status register is true, INTR is valid. There is no minimum pulse width requirement for the effective declaration of INTR.
5) IO channel ready signal IOCHRDY IO CHRDY goes low to indicate that the current I / O cycle needs to be extended. During the write cycle, IO CHRDY goes high when data is latched from the ISA bus. During the read cycle, IO CHRDY goes high when the data is valid. IO CHRDY is pulled low when reading and writing registers. The IO CHRDY pin is driven by an open collector logic gate. Therefore, this signal is pulled up to a logic high level by an internal pull-up resistor.
6) Reset signal RESET When the RESET signal is valid, the conversion module is triggered to hard restart the FPGA.
2 Working principle
As shown in Figure 1, the multi-channel control circuit based on ISA bus is composed of address coding, relay channel, optocoupler isolation circuit and so on. Its working principle is as follows: When the circuit is working, first compare the high address of the ISA bus with the board base address set by the onboard DIP switch, and its low address selects 3 read channels and 1 write channel through address coding. The read channel is the port 1 cache, port 2 cache, and port 3 readback channel, and the write channel is the port 3 cache channel. When the industrial computer needs to read the feedback signal, the feedback signal is input to the 16-channel optocoupler from the interface CN2, and its working mode is set through the resistor and the jumper module. The data is written to the port 1 buffer and the port 2 buffer for the industrial computer to read; Each optocoupler corresponds to an LED, which displays the current working status in real time. When the industrial control computer needs to send out the signal, the industrial control computer writes the data to the buffer of port 3, and after driving through the relay driver, controls 8 relays, which are output by DB1; meanwhile, each relay corresponds to an LED, which displays the current status in real time. The data written to port 3 can also be read back through the readback address, which is the same as the write address.
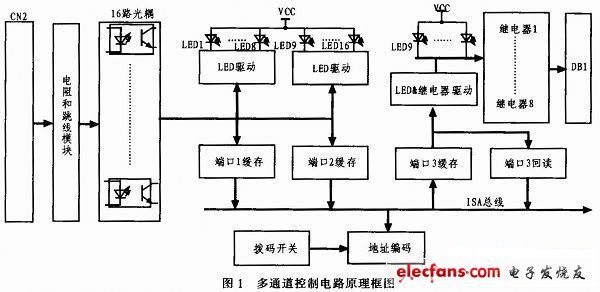
3 Circuit design
According to the working principle, the multi-channel control circuit can be divided into address coding circuit, relay control output channel circuit and optocoupler isolation input channel circuit 3 parts.
Ferrite Core Transformer,Ef 25 Transformer,Ee16 Ferrite Core Transformer,Efd Ferrite Core Transformer
IHUA INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD. , https://www.ihua-inductor.com
