Wi-Fi device shipments climbed to new heights. The Wi-Fi Alliance pointed out that in 2016, three new technologies, such as 802.11ac, 802.11ad (WiGig) and Wi-Fi LocaTIon, will have significant progress, and it is expected to attract new growth momentum for the Wi-Fi market, enabling Wi-Fi worldwide. Fi device shipments exceeded 15 billion units by the end of this year.
Phil Solis, research director at ABI Research, said the Wi-Fi market continues to grow as the Wi-Fi Alliance certification program continues to expand. Up to now, 12 billion Wi-Fi products have been shipped, and an additional 3 billion units are expected in 2016. The shipments of dual-band devices operating in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands will also increase from last year. The overall Wi-Fi market growth momentum remains undiminished.
In response to the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi technology, the Wi-Fi Alliance has developed this year's technology roadmap, including Wi-Fi performance and network capacity, as well as unique capabilities to meet the diverse connectivity needs of various applications and markets.
WiGig (802.11ad)
In the 2016 technology blueprint released by the Wi-Fi Alliance, WiGig (802.11ad) is a major development focus. The alliance pointed out that the WiGig market will grow significantly in 2016, and the technology will be complementary to 802.11ac technology, bringing multiple Gigabit (MulTI-Gigabit) transmission performance to indoor connections, resulting in multiple images such as ultra-high resolution (4K UHD). /Synchronous streaming and other applications. In the future, tri-band devices that support 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 60 GHz will provide optimal Wi-Fi performance for increasingly demanding usage scenarios.

Figure 1
Here, let's take a closer look at WiGig.
First we need to understand the concept of IEEE 802.11. IEEE 802.11 is a standard commonly used in today's wireless local area networks. It is a standard for wireless network communication defined by the International Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (IEEE). It defines the media access control layer (MAC layer) and the physical layer.
The physical layer defines two types of spread spectrum modulation methods and one infrared transmission method operating on the 2.4 GHz ISM band, and the total data transmission rate is designed to be 2 Mbit/s. The two devices can construct a temporary network by themselves, or can communicate under the coordination of a base station (Base StaTIon, BS) or an access point (AP). In order to obtain good communication quality in different communication environments, CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense MulTIple Access/Collision Avoidance) hardware communication method is adopted.
Later added two versions, 802.11a and 802.11b. The former defines a physical layer with a data transmission rate of 54 Mbit/s on the 5 GHz ISM band, while the latter defines a physical layer with a data transmission rate of 11 Mbit/s on the 2.4 GHz ISM band.
802.11ad, also known as the Wireless Gigabit Alliance (WiGig), is a wireless device dedicated to driving multi-gigabit speeds in the unlicensed 60 GHz band. Data transmission technology.
802.11ad is mainly used to realize the transmission of wireless high-definition audio and video signals in the home, and bring a more complete HD video solution for home multimedia applications. Instead of the crowded 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, 802.11ad uses the 60 GHz spectrum of the high frequency carrier. Since the 60 GHz spectrum has a large frequency available in most countries, 802.11ad can achieve simultaneous multi-channel transmission with the support of MIMO technology, and the transmission bandwidth of each channel will exceed 1 Gbps. according to
Understand the 802.11ad carrier frequency of 60GHz, the speed is 7Gbps. At the same time, 802.11ad also faces technical limitations.
For example, the 60 GHz carrier has poor diffractive power, and the signal attenuation in the air is very high, and its transmission distance and signal coverage are greatly affected, which makes its effective connection limited to a small range.
In an ideal state, 802.11ad is best suited for use as a channel for high-speed wireless transmission between devices in a room. Based on the integration of 802.11s and 802.11z, 802.11ad can be used to achieve file transfer and data synchronization between devices, and the speed will be more than 1000 times faster than the second generation Bluetooth technology. Of course, the most important use of 802.11ad is to achieve the transmission of high-definition signals.
Technical features of 802.11ad (60 GHz Wi-Fi)
WiGig technology uses the 60 GHz band, and more spectrum is available in the 60 GHz band than in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, enabling faster transmissions up to 7 Gbps by using a wider channel with a low power modulation scheme. The data transfer rate makes it ideal for indoor connections to support demanding multimedia applications including video.
Key features of the WiGig/IEEE 802.11ad specification include: maximizing performance; minimizing implementation complexity and cost; coordinating with existing Wi-Fi technology; providing advanced security.
These main features include:
1) Support data transfer rates of up to 7 Gbps;
2) Unique design supports low-power handheld devices such as mobile phones and high-performance devices such as computers, and advanced power management technology;
3) The device can be transparently switched between 802.11 networks operating in any frequency band (including 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 60 GHz);
4) Support beamforming to maximize signal strength and achieve good communication at distances up to 10 meters away;
5) Use the Galois/Counter Mode in the AES encryption algorithm for security protection;
6) High-performance wireless implementation supporting HDMI, DisplayPort, USB and PCIe.
Physical layer of 802.11ad (60 GHz Wi-Fi)
1) Spectrum and channel
The 60 GHz band does not require authorization and is widely used. As shown in Figure 2, the spectrum available in different countries varies in the 60 GHz band:
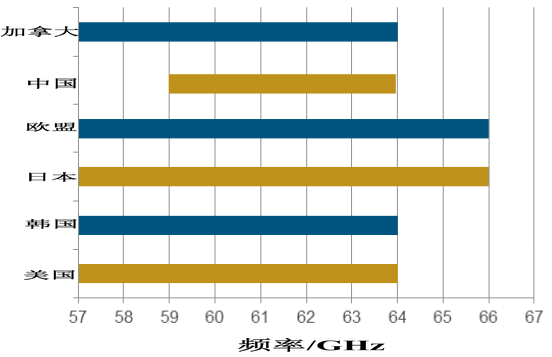
Figure 2 Available spectrum of countries in the 60 GHz band
The spectrum resources in the 60 GHz band are much richer than the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands – typically 7-8 GHz bandwidth. The 60 GHz band is also divided into multiple channels - the 802.11ad specification defines four channels, each with a channel width of 2.16 GHz.
2) Modulation and coding
The 802.11ad specification supports two types of modulation and coding schemes:
1) OFDM. The maximum transmission speed allowed is up to 7 Gbps;
2) Single carrier. Low power consumption makes it ideal for small, low-power handheld devices. The single carrier scheme supports transmission speeds up to 4.6 Gbps.
These two modulation schemes have some common elements (such as preamble and channel coding, etc.), which reduces the complexity of the implementation.
It is reported that in the future, all WiGig CERTIFIED devices must support single-carrier modulation, and some devices must also support OFDM.
MAC layer of IEEE 802.11ad (60 GHz Wi-Fi)
The new features of the IEEE 802.11ad specification's MAC layer support advanced usage models, facilitate integration with Wi-Fi networks, reduce power consumption, and provide strong security.
1) MAC architecture
As shown in Figure 3, the IEEE 802.11ad specification defines a new MAC architecture that enables two devices to communicate directly with each other, thereby developing new features (such as fast synchronization of two devices, and to a projector or television). Send audio and video data, etc.). In addition, the IEEE 802.11ad specification also supports the current 802.11 network architecture.
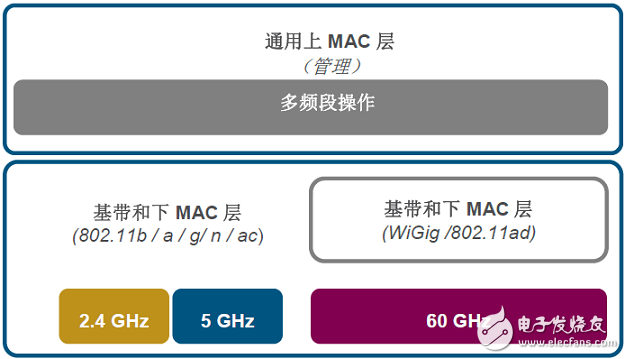
Figure 3 MAC architecture of the IEEE 802.11ad specification
2) User experience improvement technology
As can be seen from Figure 2, the IEEE 802.11ad MAC achieves a seamless fallback to 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz Wi-Fi if the 60 GHz band connection is not available, which can greatly enhance the user experience (for example, in the device from With 60 GHz switching to lower frequency Wi-Fi channels, users using Wi-Fi/WiGig integrated devices will continue to enjoy uninterrupted connectivity. Users will not only experience high performance, but will also be able to automatically utilize 60 GHz. The extra rate brought by the frequency band).
3) Power management technology
WiGig CERTIFIED devices will be able to reduce power consumption with a new predetermined access mode: two devices communicating with each other through directional connections can schedule a period of time during which they communicate, during which time the device begins to sleep. This advanced feature allows the device to perform power management more accurately based on actual traffic load - this is especially important for mobile phones and other handheld battery-powered devices.
4) Security technology
The IEEE 802.11ad specification builds on the strong security mechanisms defined by the IEEE 802.11 standard. The encryption capabilities of WiGig CERTIFIED devices are based on the government-level advanced encryption standard AES and can be implemented in hardware for high performance and efficiency.
Protocol Adaptation Layer (PAL) for 802.11ad (60 GHz Wi-Fi)
As shown in Figure 4, the Protocol Adaptation Layer (PAL) of the IEEE 802.11ad specification allows for the implementation of some standard interfaces that run directly on the MAC and PHY layers in a wireless manner:
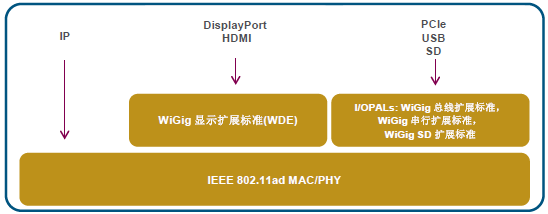
Figure 4 Protocol Adaptation Layer of the IEEE 802.11ad Specification
1) Audio/Video: WiGig Display Extension (WDE)
WDE supports wireless transmission of audiovisual data (such as transferring movies from a computer or digital camera to a television or projector). This PAL supports HDMI and DisplayPort interfaces as well as wireless implementations of high bandwidth digital content protection (HDCP) solutions for protecting digital content transmitted over these interfaces. Its scalability allows it to transmit both compressed and uncompressed video.
2) Input/output PAL: WiGig bus extension, WiGig SD extension, and WiGig serial extension
The input/output PAL defines a high performance wireless implementation of a computer interface that is widely used in the 60 GHz band. There are three types of currently defined I/O protocols (PAL): WiGig Bus Extension (PCIe), WiGig SD Extension (Secure Digital I/O), and WiGig Serial Extension (USB).
(1) WiGig bus expansion
Inside the computer, PCIe is typically used to connect the CPU and memory to an I/O controller that supports storage, network cards, and other interfaces. In addition, it can be used to connect to media and visual processors to improve image quality or offload CPU processing. The implementation of PAL supports multi-gigabit wireless synchronization between devices, as well as connections to storage and other high-speed peripherals.
(2) WiGig SD extension
SD memory cards are widely used in mobile devices to store various files such as documents, pictures, and audio and video content. The WiGig SD extension is used to access an SD memory card installed on a remote device from a host device, such as an SD memory card on a smartphone from a laptop. The WiGig SD expansion is suitable for battery-powered devices with limited resources because it optimizes the implementation process for easy storage access, and file transfer speeds can reach billions of bits, while significantly saving energy.
(3) WiGig serial extension
USB is often used to connect peripherals and other devices to the host. This USB PAL supports wireless connectivity between USB devices and facilitates the development of products such as USB extensions. The WiGig serial extension has been handed over from the Wi-Fi Alliance to the USB-IF for use as the basis for the medium-free serial bus specification.
Teaching and training meetings, classroom teaching; traditional projectors are not easy to carry. In school classrooms, due to the naughty students, projectors are not safe in the classroom and are easily damaged by students. The portability of micro projectors makes up for the teaching vacancies. In the future, teachers will give lectures. You only need to store the data in the projector to show it to students for teaching, saving the trouble of textbooks and handwriting with pens and chalks.
portable projector for teaching,portable projector education,portable classroom projector,projector for teachers
Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.happybateprojector.com
