The latest USB 3.0 protocol (or "SuperSpeed ​​USB") was developed to provide higher data transfer rates and increase power supply by supporting higher current levels on each port. It includes new power management features and new cables and connectors for backward compatibility with USB 2.0 devices. The most notable change is that four additional copper data lines are added in parallel to the existing USB 2.0 bus (as shown in Figure 1). These additional copper data lines are used to transmit ultra-high speed data, but also transmit ESD (electrostatic discharge) and other unwanted transient voltages.
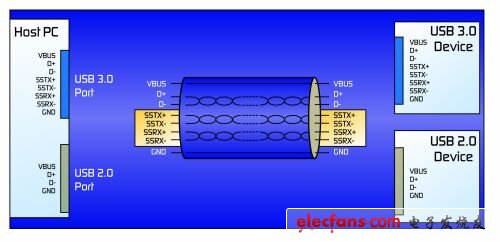
Figure 1: The revised USB 3.0 protocol adds a dual simplex data channel.
The increased current and power capability of USB 3.0 means new circuit protection schemes are needed. Improved circuit protection methods can help protect USB 3.0 applications from overcurrent, overvoltage, and ESD transients.
USB 3.0 overcurrent protection
USB 3.0 provides power through two components: a standard mainframe (Type A connector) and a new power supply (Powered-B connector). The latest SuperSpeed ​​specification increases the total amount of current available from USB devices (from 0.5A to 0.9A). The new Powered-B connector allows one USB device to charge another device with up to 1.0A. Since the overcurrent condition affects the power bus, all power supplies (such as hosts, hubs, and Powered-B devices) must provide overcurrent protection. Overcurrent protection is also required by the UL60950 standard.
Similar to USB 2.0, all types of USB 3.0 hosts must be powered. The single unit load of USB 3.0 is redefined to 150mA, which is slightly higher than the USB 2.0 100mA. Now, a USB 3.0 host must be able to support up to 6 units (900 mA) per port. In addition, USB 3.0 hubs may no longer require bus power. All USB 3.0 hubs must now support 900mA per port.
In addition, systems that support USB charging and USB 3.0 require overcurrent protection devices that can withstand higher currents. The USB charger specification uses the same pin configuration as USB 2.0, but allows for higher currents (up to 1.5A per port).
Finally, USB 3.0 defines a new Powered-B connector with the main benefit of better portability. The Powered-B connector allows removal of the USB cable and additional power. A USB device using the Powered-B connector can now power another USB device. By providing two additional jacks, the new connector allows one power supply (with a Powered-B connector socket) to deliver up to 1000mA to another device (with a Type B power connector plug). For example, a printer can power a wireless adapter, eliminating the need for a wired USB connection.
In all of these applications, the Polymer Positive Temperature Coefficient Device (PPTC) provides the most cost-effective solution for USB overcurrent protection. PPTC devices are available for USB 3.0 host applications, USB 3.0 hub applications, USB charger applications, and current limit protection in USB 3.0 Powered-B connector applications. PPTC PolySwitch devices mounted on the VBUS port of the USB power supply limit current during short-circuit conditions to prevent overcurrent damage due to sudden short circuits in downstream circuits and contribute to the UL60950 standard.
Ebang Ebit Mining Machine:Ebang Ebit E11++,Ebang Ebit E9,Ebang Ebit E9.2,Ebang Ebit E9+,Ebang Ebit E9i,Ebang Ebit E11+,bang Ebit E10,Ebang Ebit E11
Ebang is a blockchain production company specializing in the production of Bitcoin machines. Their ebit series has always been a cost-effective series of Bitcoin machines, with stable income, low machine loss and guaranteed after-sales service.
Ebang Ebit Mining Machine,E9 25Th/S Miner,ebit miner,ebit mining machine,ebang miner
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hkcryptominer.com
