SONET / SDH optical network concept
SONET is the abbreviation of synchronous optical fiber network. It was originally proposed by Bellcore in the 1980s, and the first optical networks began to appear since then. It is now an ANSI standard for optical fiber transmission systems. The SONET standard for defining interfaces is located at the physical layer of the OSI seven-layer model structure. This standard defines the interface rate hierarchy and allows data to be multiplexed at many different rates. ITU adapted SONET to SDH, which became the world standard for building optical communication networks. SONET is now considered a subset of SDH, but the term "SONET / SDH" is common in North America. Because of SONET / SDH, the copper-oriented digital system extends into the optical field, although the system is based on OC (optical carrier). The SONET / SDH core maps ATM cells into SONET or SDH frame format and transmits them to the destination, and then extracts them as ATM cells during data reception. Because the cell length is short and fixed, the delay in switching between each network node is very small.
The basic block structure of SONET is STS-151.84Mb / s signal, which is suitable for loading 1 DS-3 signal. SONET system reaches STS-48, that is, 48 ​​channels of STS-1 signals, capable of transmitting 32256 channels of voice signals, with a capacity of 2488.32Mb / s, where STS stands for electrical signal interface, and the corresponding optical signal standards are expressed as OC-1, OC- 2 etc.
The figure depicts a SONET / SDH network. The small access ring network is connected to a larger area or backbone ring network, and then connected to the regional and national ring networks in turn. The transfer from the small ring network to the large ring network involves a transition to a higher OC level. The access ring network usually runs on OC-3 (l55Mbit / s). These ring networks are imported into OC-12 (622Mbit / s) or OC-48 (2.4Gbit / s) regional loops, and then transferred to OC-96 (4.9Gbit / s) or OC-192 (lOGbit / s) The backbone ring network. As shown in Figure N-7, the ring network is interconnected by ADM (add-drop multiplexer) and DCS (digital cross-connect). In addition, PoP devices are interconnected with the access ring network through add-drop multiplexers. The photoelectric and electro-optical conversion occurs at the connection point. The digital level cross-connect within the PoP provides a connection point for voice and data communications.
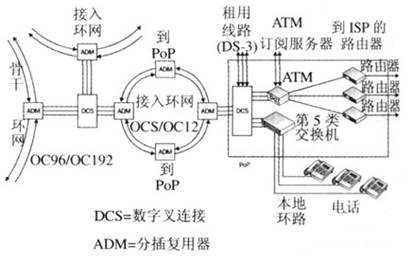
Figure SONFF optical network ring and carrier PoP (point of presence) components
ADM uses time slot exchange to achieve broadband management, which allows different VCs between two STM-N signals to be interconnected, and has various interface signals (PDH) specified by G.703 without tapping and terminating the overall signal. ) Or STM-N signal (SDH) access STM-M (M> N) for any branch. It does not terminate and demultiplex the entire range of signals on an optical cable, but divides / inserts sub-rate signals. If a signal needs to be switched to another ring network, it is separated from one ring network and inserted into another ring network. For SONET, this means performing "optical-electrical-optical" conversion.
SHAOXING COLORBEE PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.fantaicolorbee.com
