And the current is facing? What do you mean?
Haha, this is a cow temper of the inductance component. It is this cow temper that you can't leave it in many places!
Or start by understanding the inductance! The actual construction of the inductor is very simple. Taking an enameled wire into a coil is an inductor! Using magnetic blocks to make the enameled wire around is the magnetic bead pole, which is common in mpn:

In the circuit diagram, the inductance is generally expressed by L. Just as the resistor is R and the capacitor is represented by C, you can see which component in the circuit diagram is marked with L next to it and use the symbol:
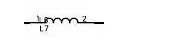
To express the inductance, what needs to be noted here is that it should be like this:
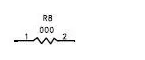
The symbol is different. This symbol is a representation of resistance. Don't think of it as an inductor!
The inductance is not divided into positive and negative poles. In the circuit, it is not necessary to be connected to which side is connected to the positive side. In some places, it is divided into phases, that is, the coil of the inductor is wound, and mpn does not need to be considered! The size of the inductor is based on "Henry", referred to as Hen (H), and the smaller units are millihenry (mH) and microhenry (uH), which are in thousands of conversions!
What is the temper of the inductor?
Why do you say that it is working against the current? It turns out that the inductor is in the circuit. When the current wants to pass through it, it will generate a voltage of its own. The current direction of this voltage is just the opposite of the direction of the current to be passed. But this is only a matter of moments, and then there is no such resistance!
When the current through the inductor in the circuit is going to be broken, the inductor generates a voltage that produces the opposite current to the current to be disconnected—it doesn't let the current break! It's topping the cow, haha. , saying that it and the current are not grievances against it?
It’s this kind of temper of inductance that allows us to use it to play a certain role. Think about it. We talked about the alternating current in the circuit that has a changing direction. This exchange is constantly changing. Sometimes we You don't need it. Sometimes we need it. The smart human is naturally thinking of the temper of using the inductor. The direction of the alternating current is constantly changing, and the inductance is constantly resisting. As a result, the alternating current in the direction cannot pass the inductor. Since the direct current does not change in the direction of the current, the current can pass through the inductor smoothly. The magnitude of the inductance is not the same as that of the fast change of the alternating current. The same inductor blocks the fast changing current and blocks the alternating alternating current. Small; for the same change speed of the AC, the sense of large value is large, and the small value of the sense is small!
By using the character of the inductor, we can easily separate the alternating current and the direct current in the circuit! It is possible that everyone thinks of the capacitor here. The characteristic of the capacitor is "DC blocking, AC", then the characteristics of the inductor are just and The opposite of the capacitor: AC, DC, and the circuit is due to the organic coordination of the inductor and capacitor, so that the AC and DC in the circuit are easy to open separately! Of course, this feature of the inductor has some other functions, which require you to upgrade and learn, and slowly understand!
Upgrade theory: To learn thoroughly about the theory of inductance, we must carefully learn to get through the "Law of the Times"!
What is an inductor? Inductors (inductors) and transformers are electromagnetic induction components that are wound with insulated wires (such as enameled wire, yarn wrapped wire, etc.) and are one of the commonly used components in electronic circuits.
First, self-inductance and mutual sensation
(1) Self-inductance
When a current flows through the coil, a magnetic field is generated around the coil. When the current in the coil changes, the surrounding magnetic field also changes accordingly. The changed magnetic field can cause the coil itself to generate an induced electromotive force (the electromotive force is used to indicate the terminal voltage of the ideal power source of the active component), which is self-inductance.
(2) Mutual sense
When the two inductor coils are close to each other, the change in the magnetic field of one inductor coil will affect the other inductor coil. This effect is mutual inductance. The magnitude of the mutual inductance depends on the degree to which the inductance of the inductor is coupled to the two inductors.
Second, the role of the inductor
The main function of the inductor is to isolate, filter or form a resonant circuit with capacitors, resistors, etc.; boost, buck is often inseparable from it!
Now analyze several inductive circuits and analyze their respective roles in the circuit:
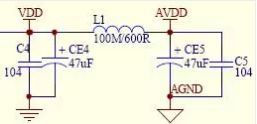
Figure 1
Figure 1 is a vcc and avcc power filter circuit in mp3, vcc and avcc voltage are 3v, vcc is for the main control power supply, requires voltage stability and is a pure DC component, does not allow AC components! avcc is given The audio amplifier circuit provides energy, and it needs to have enough DC energy supply! It may be asked, why should the two voltages be connected to an inductor L1 even if it is 3v?
When the audio amplifier circuit amplifies the sound, with the high-pitched bass and the small-tone change, the required current will change dramatically. The inductance and capacitance are opposite in temper, but there is a common place where the voltage across the inductor and capacitor cannot be Mutation, so the inductance L1 and the capacitance on both sides have a function of stabilizing the vcc and avcc voltages, that is, the voltage fluctuation caused by the sound amplification does not affect the fluctuation of the vcc voltage supplied to the main control work;
In addition to this effect, there is a second effect from L1 and the capacitors on both sides, that is, the filtering effect. Since the sound amplifying circuit is easy to mix into the AC component, the AC component must never enter the vcc voltage and enter the master control. L1 is the main component to prevent the entry of AC components. The blocked AC component cannot pass through L1, so it has to disappear through C5 and CE5 into the ground! The circuit consisting of C5 and CE5+L1+C4 and CE4 is also called “π-type†filter!
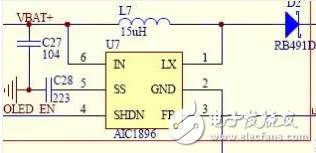
Figure II
Figure 2 is the screen backlight boost circuit in the mp3 circuit. The screen backlight in mp3 is usually connected by 2-3 LED tubes. The LED tube needs 3v DC voltage. Light up, 2 strings need 6v voltage, 3 strings will be 9v voltage can be fully lit! We know that the highest voltage of lithium battery in mp3 is 4.2v, the normal working voltage is only 3.7v, this voltage is fundamental There is no way to light up more than two LED tubes connected in series, so you must raise the voltage of 3.7v to 6v or 9v to light the LED tube!
The above circuit is such a boost circuit. In the circuit, U7 is a boosting integrated block, which combines with L7, C28, etc. to form a oscillating elevated AC voltage, and then the D2 component (called diode, we will talk about its role in the next lecture) The alternating current turns into a direct current to light the LED tube! So the L7 inductor here is the boost resonant inductor!
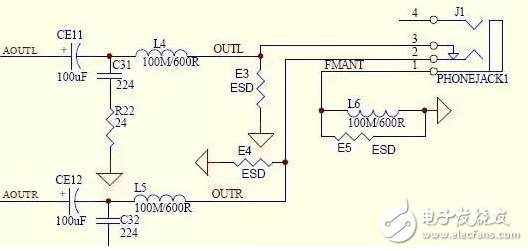
Figure III
Figure 3 shows that the mp3 headphone circuit has three magnetic bead inductors, L4, L5 and L6. L4 and L5 are used to block the AC component (called ultrasonic wave) that is too fast to be heard in the sound, and let it pass through the capacitor. C31, C32 into the ground, no longer enter the headphones let us feel the sound is not pure and tired! We know that the mp3 radio antenna uses the headphone cable as the antenna. The function of the magnetic bead inductor of L6 is to block the radio wave signal sent from the headphone cable from entering the ground and only entering the antenna receiving pin of the FM radio block!
In Figure 3, the 6-pin of U7 is the power input pin, the 5 pin is the unloading, the 4 pin is the working state of the control U7, the high-potential (with voltage) when the working screen backlight is on, the low-potential 0v stops working, the screen background The light is off, the power saving state; 3 feet are output compensation, 2 feet are grounded, and 1 pin is connected to the inductor oscillation output. When the inductance value is constant, the faster the oscillation speed, the faster the current direction changes, and the higher the output voltage! In Figure 3, R22 is the compensation resistor E3, E4, E5 is the electrostatic high-voltage discharge resistor, you can not connect!
Engine Parts oil tube,Engine Parts water pipe,Engine Parts exhaust pipe,Engine Parts Rubber Pipe
Chongqing LDJM Engine Parts Center , https://www.ckcummins.com
