 First, the midpoint potential (point C potential) is EC / 2. Second, BG2 and BG3 provide a certain forward bias voltage.
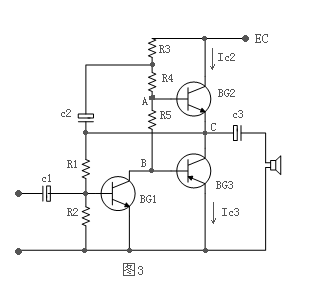
First, the midpoint potential (point C potential) is EC / 2. Second, BG2 and BG3 provide a certain forward bias voltage. First adjust the voltage VC at point C. R3, R4, and R5 in Figure 3 are the collector resistors of BG1, where R3 and C2 form a bootstrap circuit, and R5 is to provide bias to BG2 and BG3. In order to avoid BG2 and BG3 having too large collector current when adjusting VC, the collector current of BG3 is too large. R5 and R2 are the bias current resistors of BG1. Adjust R1 so that VC = EC / 2.
Then adjust the working current of BG2 and BG3. As can be seen from Figure 3, the emitter voltages of BG2 and BG3 are determined by the voltage across R5, that is, VA-B = VBE1 + VBE2, so as long as the size of R5 can be adjusted, BG2 can be adjusted. , The purpose of BG3 working current. During the actual adjustment, because the value of R5 is very small, a 100-ohm potentiometer can be used instead. Connect the ammeter in series between the collector of BG2 and EC. While adjusting the potentiometer, observe the indication of the ammeter so that the current indication is 5-10 Milliamps.
It should be noted that the currents of VC, BG2 and BG3 will influence each other when adjusting. After VC is adjusted, adjust IC2. When IC3, VC will change again. Therefore, adjust R1 again to make VC return to the value of EC / 2. When adjusting R1, it changes IC2 and IC3, so it needs to be adjusted several times.

Follow WeChat
Interesting and informative information and technical dry goods

Download Audiophile APP
Create your own personal electronic circle

Follow the audiophile class
Lock the latest course activities and technical live broadcast
comment
Publish
related suggestion
